xEVs
Types of Electric Vehicles (xEVs)
Electric vehicles encompass various technologies that use electricity as part of their propulsion system. Here's a detailed breakdown of the main types:
1. Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)

- FCEVs use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity that powers electric motors.
- The fuel cell combines hydrogen from an onboard tank with oxygen from the air to produce electricity, water vapor, and heat.
- A small battery is present onboard to ensure sudden boost power is available on demand
- The Fuel Cell will charge this battery, which will then power the motor
- Even though battery is present, the fuel source is Hydrogen, which generates the electricity needed for EV, hence they are called FCEVs
- Since the one of the main benefits of the Hydrogen Fuel System is quick refill times, plug-in charging for the electric battery is usually not provided
Key Characteristics: - Zero direct emissions (only water vapor)
- Hydrogen storage in high-pressure tanks (typically 350-700 bar)
- Quick refueling (3-5 minutes)
- Longer range compared to most BEVs (300-400+ miles)
- Electric drivetrain with fuel cell as primary power source
Advantages: - Fast refueling similar to conventional vehicles
- No battery degradation concerns
- Excellent range and performance in cold weather
- Zero local emissions
Challenges: - Limited hydrogen infrastructure
- High vehicle costs
- Hydrogen production and distribution complexity
- Lower overall efficiency compared to BEVs
Examples: Toyota Mirai (limited trials), Hyundai NEXO (pilot programs), Tata Motors and Mahindra developing FCEV commercial vehicles
2. Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
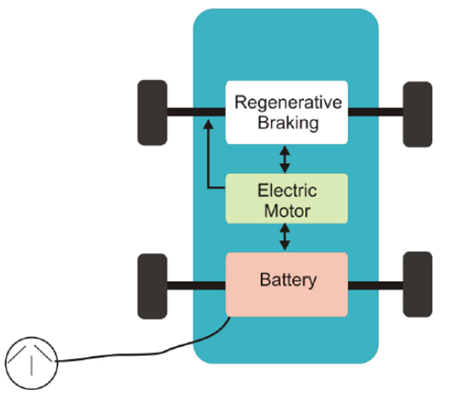
- BEVs are powered entirely by electricity stored in large battery packs, typically lithium-ion.
- Electric motors provide propulsion with no internal combustion engine.
Key Characteristics: - 100% electric propulsion
- Large battery capacity (typically 40-100+ kWh)
- Charging via AC/DC charging stations
- Regenerative braking for energy recovery
- No tailpipe emissions
Advantages: - Highest energy efficiency among all vehicle types
- Zero local emissions
- Lower operating costs
- Quiet operation
- Instant torque delivery
- Minimal maintenance requirements
Challenges: - Longer charging times compared to refueling
- Range limitations (though improving)
- Battery degradation over time
- Higher upfront costs
- Charging infrastructure dependency
Examples: Tata Nexon EV, Tata Tigor EV, MG ZS EV, Hyundai Kona Electric, BMW iX, Mercedes EQC, Audi e-tron
3. Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
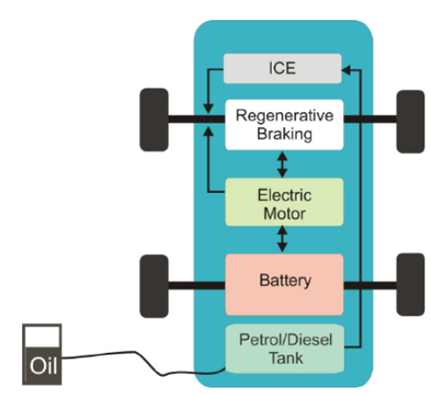
- HEVs combine an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor and battery system.
- The vehicle cannot be plugged in to charge; the battery is charged through regenerative braking and the ICE.
Key Characteristics: - Dual propulsion system (ICE + electric motor)
- Small battery pack (typically 1-3 kWh)
- No external charging capability
- Automatic switching between power sources
- Improved fuel efficiency over conventional vehicles
HEV Classifications:
3.1 Parallel Hybrid
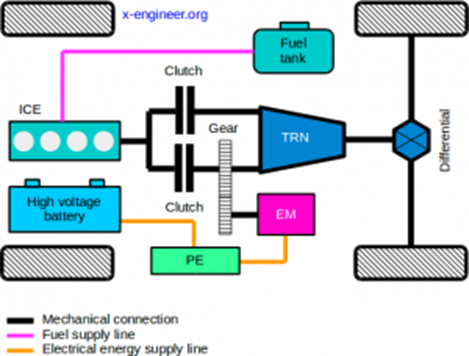
- Configuration: Both the ICE and electric motor can directly drive the wheels, either independently or together.
Operation: - ICE and electric motor connected to the transmission
- Both power sources can propel the vehicle simultaneously (Torque Assist/Boost)
- Electric motor assists ICE during acceleration
- Engine stop & start
- Engine driving mode (typically at speeds higher than 40kmph)
- Electric driving mode (typically at speeds lower than 40kmph)
- Most common hybrid configuration
Advantages: - Efficient at highway speeds
- Good power delivery
- Relatively simple control system
Disadvantages - Less smooth operation compared to series hybrids, especially during transitions between electric and ICE power
- Limited electric-only capability, especially at higher speeds
- ICE operates at varying efficiency levels since it's mechanically connected to the wheels, unlike series hybrids where it can run at optimal RPM
- Less effective in stop-and-go city traffic where series hybrids excel
Examples: Maruti Suzuki Grand Vitara (strong hybrid), Toyota Urban Cruiser Hyryder
3.2 Series Hybrid

- Configuration: Only the electric motor drives the wheels. The ICE acts solely as a generator to charge the battery.
Operation: - ICE disconnected from wheels
- ICE runs at optimal efficiency to generate electricity
- Electric motor provides all wheel power (Electric driving mode)
- Engine stop & start
- ICE can be turned off when battery has sufficient charge (Charge at standstill)
Advantages: - ICE operates at optimal efficiency
- Excellent low-speed performance
- No need for a gearbox transmission
- Smooth operation (no mechanical connection between ICE and wheels)
Disadvantages - Since engine is running at constant speed for maximum efficiency, at higher vehicle speeds, there can be loss in performance as power is dependent on battery reserves.
- Both electric machines (Generator & Motor) need to have similar power rating as the internal combustion engine. double energy conversion losses.
- Adds a lot of system weight and volume, as one is basically fitting a full size engine, motor and generator
Examples: BMW i3 REx (limited availability), Nissan e-Power technology (expected in future models), Honda City Hybrid
- A special category of series hybrids that primarily operate as BEVs with a small ICE "range extender" that activates only when the battery is depleted.
- These vehicles have larger batteries than traditional hybrids (similar to PHEVs) but the ICE cannot directly drive the wheels - it only generates electricity.
- The battery on a single charge can easily provide about 70% of the total usable range of the vehicle before using Range Extending Engine
- Examples include BMW i3 REx and Mazda MX-30 R-EV.
- In India, this technology is being explored by various manufacturers for future models.
3.3 Series-Parallel Hybrid

- Configuration: Can operate in both series and parallel modes depending on driving conditions. Tries to combine the best of both technologies.
Operation: - Planetary gear system allows flexible power routing
- Low speeds: typically series mode (electric motor only)
- Highway speeds: typically parallel mode (ICE drives wheels)
- High power demand: combined mode (both ICE and motor - Torque assist/boost)
- Engine stop & start
- Can Charge at standstill
Advantages: - Optimal efficiency across all driving conditions
- Maximum flexibility in power management
- Best overall fuel economy potential
Disadvantages - Most sophisticated hybrid system
- More cost and more failure points due to complexity
- More Weight and additional engineering to combine to systems
Examples: Toyota Camry Hybrid, Toyota Vellfire (imported), Lexus ES 300h, Lexus NX 350h, Toyota Prius
4. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- PHEVs combine features of HEVs and BEVs.
- They have larger batteries than HEVs and can be charged from external power sources, allowing for electric-only driving for limited distances.
- Simply put, they are HEVs that can be charged using an external AC/DC charger
Key Characteristics: - Larger battery pack than HEVs (typically 8-20 kWh)
- External charging capability
- Electric-only range (typically 20-60 miles)
- ICE backup for extended range
- Can operate as BEV for short trips, HEV for longer trips
Advantages: - No range anxiety
- Electric driving for daily commutes
- Fuel backup for long trips
- Lower emissions than conventional vehicles
- Potential for zero local emissions during electric-only operation
Challenges: - More complex than HEVs or BEVs
- Higher cost than HEVs
- Requires charging infrastructure for optimal benefit
- Heavier than conventional vehicles due to dual systems
Examples: BMW X5 xDrive45e, Mercedes-Benz GLE 350de, Volvo XC90 T8 (limited luxury segment availability)
- PHEVs are HEVs with a slightly larger battery
- The total pure electric driving range is less than 50% of total drivable range
- REEVs are BEVs with a small engine present to extend range
- The total pure electric driving range is more than 70% of total drivable range
Summary Comparison
| Vehicle Type | Battery Size | External Charging | ICE Present | Electric Range | Total Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCEV | Small | No | No | 480-640+ km | 480-640+ km |
| BEV | Large | Yes | No | 240-640+ km | 240-640+ km |
| HEV | Small | No | Yes | 1.6-3.2 km | 640-960 km |
| PHEV | Medium | Yes | Yes | 32-96 km | 640-960 km |
- Each xEV type serves different use cases and consumer needs, with the choice depending on factors like driving patterns, charging availability, budget, and environmental priorities.
- Refer to EV Basics L1 A#Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) on how these choices are influencing the global environmental impacts
Academic Sources:
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Energy Management Strategies - IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Review - International Journal of Hydrogen Energy
- Battery Electric Vehicle Energy Consumption Modeling - Applied Energy Journal
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Control Strategy - IEEE Control Systems Magazine
Research Institutions: